
12 STRIKING FACTS ABOUT DUNG BEETLES
Dung beetles are often used as model organisms in biology and ecology and they have charismatic behavioral and biological features, which make them stand out among other animals. The peculiarity of dung beetles can be quickly comprehended from the most striking facts about them summarized below.


-
With over 6000 species of which 30–50% are still undescribed, dung beetle diversity exceeds the diversity of extant mammals (~5500 species) and approaches that of birds (~9800 species).
-
Besides impressive species diversity, dung beetles are also impressively abundant: a single pile of fresh elephant dung can contain up to 7000 scarabaeine individuals.
-
Dung beetles are the only known animals, beside humans, that use the Milky Way for navigation (Dacke et al., 2013)
commons. wikimedia.org, en.wikipedia.org

commons. wikimedia.org
-
The Australian dung beetle project is worth special attention. Native Australian dung beetles are adapted to only feed on the dung of marsupials, the native Australian mammals. The native dung beetles were not able to utilize the dung of cattle that was relatively recently introduced to Australia by the Europeans. Undecomposed dung began to accumulate on pastures in high amounts, which stimulated pollution, uncontrolled breeding of pestilent flies and worms and the reduction of grazing areas for cattle. To fight this problem, dung beetles from Africa, which were capable of utilizing cattle dung, were introduced to Australia (Bornemissza, 1976).


-
Dung beetles are extremely popular beetles in science: they are the second most cited subfamily of beetles on Google Scholar (Tarasov and Genier, 2015).
-
The global ecosystem service of dung recycling provided by dung beetles is valued at $380 million annually in the US (Losey and Vaughan, 2006).
-
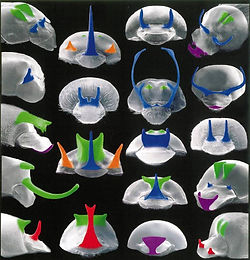
Male competition armed some species of dung beetles with extravagant head horns. The scarabaeine genus Onthophagus, due to the dramatic diversity of horns among its species, is used as a model group in developmental biology and ecological development (Scholtz et al., 2009a; Moczek, 2011).
Emlen et al., 2005; Evolution

-
Cheap collection and processing of dung beetle samples single out these beetles among other invertebrates for various types of ecological studies (Gardner et al., 2008).
-
The IUCN Red List Index program selected dung beetles, amongst few other invertebrate taxa, to measure the risk of biodiversity loss worldwide (Baillie et al., 2008; Nichols and Gardner, 2011).
-
Dung beetles, due to their ecological sensitivity, are used for assessing human impact (Spector, 2006; Scholtz et al., 2009b).


-
Beside utilization of animal excrements, dung beetles provide a number of other important ecosystem services, namely, they are involved in nutrient cycling, bioturbation, enhancement of plant growth, secondary seed dispersal, parasite suppression, fly control, trophic regulation and pollination (Nichols et al., 2008).
-
Dung beetles, based on their behavior, are classified into tunnelers, dwellers and rollers. The first two bury dung beneath dung pads and live inside dung, respectively. The third are the most remarkable of them all; the rollers roll dung into balls and then bury the ball away from the dung pad for feeding and breeding needs, a behavioral trait that made them (namely Scarabaeus) a sacred animal in ancient Egypt.

ccmaknowledgebase.vic.gov.au tunnels
References
-
Baillie, J. E., Collen, B., Amin, R., Akcakaya, H. R., Butchart, S. H., Brummitt, N., Meagher, T. R., Ram, M., Hilton‐Taylor, C., Mace, G. M. 2008. Toward monitoring global biodiversity. Conservation Letters 1, 18-26.
-
Bornemissza, G. 1976. Australian dung beetle project, 1965-1975. AMRC Rev Aust Meat Res Comm.
-
Dacke, M., Baird, E., Byrne, M., Scholtz, Clarke H., Warrant, Eric J. 2013. Dung Beetles Use the Milky Way for Orientation. Current Biology 23, 298-300.
-
Gardner, T. A., Barlow, J., Araujo, I. S., Ávila‐Pires, T. C., Bonaldo, A. B., Costa, J. E., Esposito, M. C., Ferreira, L. V., Hawes, J., Hernandez, M. I. 2008. The cost‐effectiveness of biodiversity surveys in tropical forests. Ecology letters 11, 139-150.
-
Moczek, A. 2011. Evolution and development: onthophagus beetles and the evolutionary developmental genetics of innovation, allometry and plasticity. Dung beetle ecology and evolution. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, 126-151.
-
Nichols, E., Spector, S., Louzada, J., Larsen, T., Amezquita, S., Favila, M. E. 2008. Ecological functions and ecosystem services provided by Scarabaeinae dung beetles. Biological Conservation 141, 1461-1474.
-
Nichols, E. S., Gardner, T. A. 2011. Dung beetles as a candidate study taxon in applied biodiversity conservation research. Ecology and evolution of dung beetles, 267-291.
-
Scholtz, C. H., Davis, A. L. V., Kryger, U. 2009a. Evolutionary biology and conservation of dung beetles. Pensoft Pub.
-
Scholtz, C. H., Davis, A. L. V., Kryger, U. 2009b. Evolutionary biology and conservation of dung beetles. Pensoft Sofia, Bulgaria.
-
Spector, S. 2006. Scarabaeine dung beetles (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae): an invertebrate focal taxon for biodiversity research and conservation. Coleopterists Society Monographs Patricia Vaurie Series 5, 71-83.
-
Tarasov, S., Génier, F. 2015. Innovative Bayesian and Parsimony Phylogeny of Dung Beetles (Coleoptera, Scarabaeidae, Scarabaeinae) Enhanced by Ontology-Based Partitioning of Morphological Characters. PLoS ONE 10, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116671.

